Abstract / Introduction / Summary:
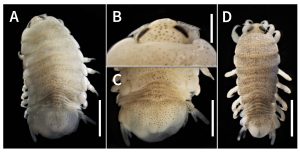
Specimens (10 ovigerous females and nine adult males) of cymothoid isopod were collected in October 2022 from the branchial cavity of Japanese halfbeak, Hyporhamphus sajori (Temminck and Schlegel, 1846), in coastal waters of Tsuruga Bay, an inlet of the southern Sea of Japan, Fukui Prefecture, central Japan. Prevalence of isopod infection was 36% (28 fish examined, 202–225 mm total length), and paired female-male isopods were found on each infected fish, excluding one fish harboring only one female isopod. The morphological features and body length (female, 10.5–15.0 mm; male, 9.1–10.2 mm) of the isopod specimens nearly correspond to the original description of Mothocya parvostis Bruce, 1986, and they are herein identified as this species. Nonetheless, Mothocya sajori Bruce, 1986 is also known to infect Japanese halfbeak in Japanese waters, and it is necessary to clarify whether M. parvostis and M. sajori are conspecific because specimens of Mothocya, which are morphologically similar to but differ in body length from both species, were previously collected from Japanese halfbeak in Japan. Moreover, it is also desirable to study the morphology of cymothoid reported as Mothocya sp. (originally described as Iroha [sic] melanosticta japonensis Avdeev and Avdeev, 1974) or M. parvostis from Pacific saury, Cololabis saira (Brevoort, 1856), in the seas around Japan.
